Stack 🆚 Queue
📌 Common feature
1
2
the ways to use 'Linear structure'
( + 'List, LinkedList )
📌 Let’s compare
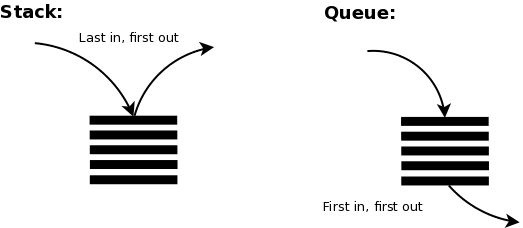
| Stack | Queue | |
|---|---|---|
| Feature | LIFO (Last In Fisrt Out) | FIFO (First In First Out) |
| Input / Output | push(data) / pop() | enQueue() / deQueue() |
| Parts | - | front : the part only remove data / rear : the part only insert data |
| Situations | Stack can be used in most situations | Queue is used in situations where data needs to be processed in order of the time. |
| Examples of situation | - undo - make the strings in reverse order | - BFS (Breadth-First Search) - waiting process |
| Implementation | Stack, ArrayDeque | LinkedList, ArrayDeque |
| Useful algorithm | DFS (Depth-First Search) | BFS (Breadth-First Search) |
⭐️ Methods in Java8
Stack

Queue

📌 Implementation
Stack
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
import java.util.Stack;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
Stack<String> stack1 = new Stack<String>();
// = Deque<String> stack1 = new ArrayDeque<String>(); for complex and speedy stack
// push()
stack1.push("A");
stack1.push("B");
stack1.push("C");
List<String> list = stack1.stream().collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println("Stack1 : " + list); // Stack : [A, B, C]
// pop()
System.out.println(stack1.pop()); // [C] & delete it
System.out.println(stack1); // [A, B]
// clear()
stack1.clear();
System.out.println(stack1); // null
//******
Stack<Integer> stack2 = new Stack<>();
// push()
stack2.push(5);
stack2.push(2);
stack2.push(7);
// peek()
System.out.println(stack2.peek()); // 7 -> only return the last data
System.out.println(stack2); // [5, 2, 7]
// size(), empty(), contains()
System.out.println(stack.size()); // 3
System.out.println(stack.empty()); // false
System.out.println(stack.contains(1)); // false -> check there is '1' in stack, contains(int value)
// search()
System.out.println(stack.search(2)) // 2 -> return index
System.out.println(stack.search(5)) // 1
Queue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.LinkedList;
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
// = Deque<String> qu = new ArrayDeque<String>(); for complex and speedy queue
// add()
queue.add(5);
queue.add(1);
queue.add(2);
queue.add(3);
queue.add(4);
queue.forEach((value)->{ System.out.print(value);}); // 51234
// poll()
System.out.println(queue.poll()); // 5 & delete it
System.out.println(queue); // [1,2,3,4]
System.out.println(queue.poll()); // 1 & delete it
System.out.println(queue); // [2,3,4]
// peek()
System.out.println(queue.peek()); // 2
System.out.println(queue); // [2, 3, 4]
// remove()
queue.remove(3);
System.out.println(queue); // [2, 4]
Suddenly, I come up with ‘Stack overflow’ and me when I studied for OCPJP lol

Comments powered by Disqus.