What is fibonacci numbers?
1
2
3
4
5
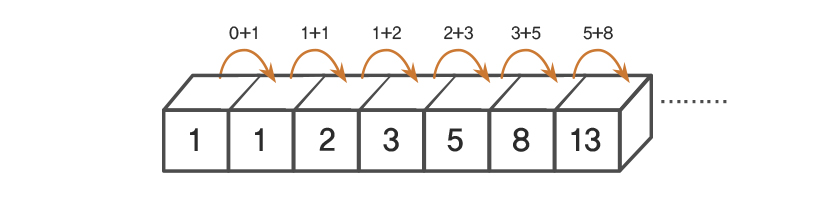
1️⃣ The first two numbers in the Fibonacci sequence are 0 and 1,
and each subsequent number is the sum of the previous two.
2️⃣ Enumeration of the Fibonacci numbers can be done faster simply
by using a basis of dynamic programming
###Example not efficient Finding Fibonacci numbers recursively.
1
2
3
4
def fibonacci(n):
if (n <= 1):
return n
return fibonacci(n - 1) + fibonacci(n - 2)
###Example efficient Finding Fibonacci numbers dynamically. (by using a basis of dynamic programming)
The time complexity of this algorithm is O(n).
1
2
3
4
5
6
def fibonacciDynamic(n):
fib = [0] * (n + 2) # initialization
fib[1] = 1 # fib[0] = 0
for i in xrange(2, n + 1): # memozation
fib[i] = fib[i - 1] + fib[i - 2]
return fib[n]
+ Then, what is dynamic programming?
1
2
3
4
1️⃣ An algorithmic technique for solving an optimization problem
by breaking it down into simpler subproblem
2️⃣ Store the result of subproblems and reuse it
The point
- #####
⭐️ Memoization - store the results of expensive function calls and returning the cached result when the same inputs occur again.
#####⭐️ VS 'Divide and conquer algorithm'
Common feature1 2
solve an optimization problem by breaking it down into simpler subproblem
Difference- ```
- the divide and conquer
- ```
- combines the solutions of the sub-problems to obtain the solution of the main problem
- dynamic programming
- uses the result of the sub-problems to find the optimum solution of the main problem ```
Tasks
1. FibFrog in codility (Lesson 13)
: Count the minimum number of jumps required for a frog to get to the other side of a river.
It’s quite difficult lol🥲
Question
https://app.codility.com/programmers/lessons/13-fibonacci_numbers/fib_frog/
Answer
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
class Solution {
private int[] fibArray;
public int solution(int[] A) {
int N = A.length;
makeFibArray(N);
int fibLength = fibArray.length;
int result = -1;
for (int i = 0; i <= N; i++) { // i : for A array
if (i == N || A[i] == 1) {
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int j = 0; j < fibLength && fibArray[j] <= i + 1; j++) { // j : for fibArray
final int start = i - fibArray[j];
if (start == -1) min = 1;
else if (A[start] > 0) {
if (A[start] + 1 < min) min = A[start] + 1;
}
}
if (i < N) {
if (min == Integer.MAX_VALUE) A[i] = 0;
else A[i] = min;
}
else { // i == N : arrived
if (min != Integer.MAX_VALUE) result = min;
}
}
}
return result;
}
private void makeFibArray(int N) {
fibArray = new int[N < 2 ? 2 : N + 1];
fibArray[0] = 1;
fibArray[1] = 2;
for (int i = 2; fibArray[i - 1] <= N; i++)
fibArray[i] = fibArray[i - 1] + fibArray[i - 2];
}
}

Comments powered by Disqus.