Big-O notation
📌 What is it?
a mathematical notation that describes the limiting behavior of a function when the argument tends towards a particular value or infinity.
In computer science, big O notation is used to classify algorithms according to how their run time or space requirements grow as the input size grows.
Time complexity + Space complexity
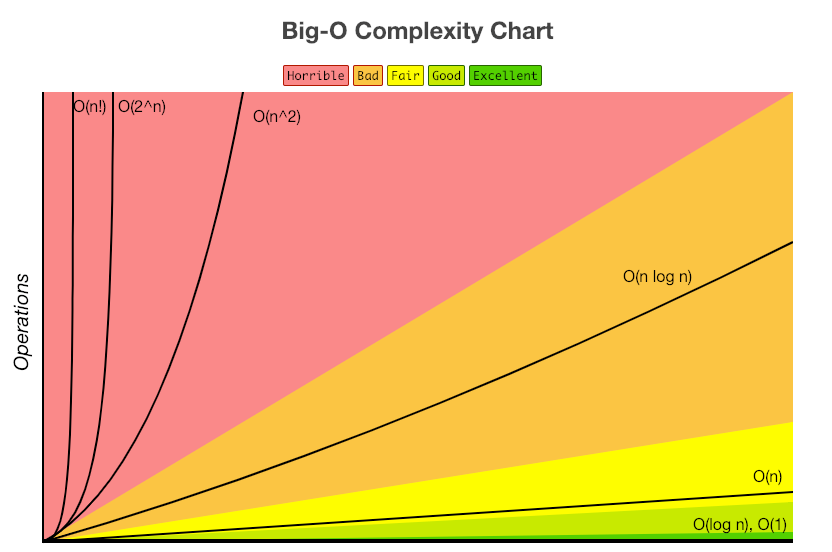
📌 Let’s compare
O(1) < O(log n) < O(n) < O(n * log n) < O(n²) < O(n³) < O(2^n) < O(n!)
And, Big-O notation ignores the following case
- O(2N) -> O(N)
- O(N² + 2) > O(N²)
- O(N² + N) -> O(N²)
📌 Example
Time complexity
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
// O(1)
int sum1(int N) {
return N * N;
}
// O(2N) => O(N)
int sum2(int N) {
sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
sum = sum + N;
}
return sum;
}
// O(N²)
int sum3(int N) {
sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= N; j++) {
sum = sum + 1;
}
}
return sum;
}
Space complexity
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
// O(N)
// recursion
int sum(int N) {
sum = 0;
if (N < 1)
return 0;
return N + sum(N - 1);
}
// O(1)
int mainSum(int N) {
int result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
result += sum(i, i + 1);
return result;
}
int sum(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
📌 Time complexity
Binary search
O(logN)
Example1. Find the square root (√)


1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
// O(logN)
public static int squareRootBSearch(int n) {
int min = 0;
int max = n;
int guess;
while (min <= max) {
guess = (min + max) / 2;
if (guess * guess == n)
return guess;
else if (guess * guess > n)
max = guess - 1;
else
min = guess + 1;
}
return -1;
}
// not binary search
// O(N)
public static int squareRootLoop(int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (i * i == n)
return i;
return -1;
}
Sorting algorithm
- Efficient but not simple algorithm
- quick sort(1), heap sort(3), merge sort(2)

The source :
https://cjh5414.github.io/big-o-notation/
https://cjh5414.github.io/binary-search/
https://velog.io/@gillog/시간복잡도
https://gmlwjd9405.github.io/2018/05/10/algorithm-quick-sort.html

Comments powered by Disqus.