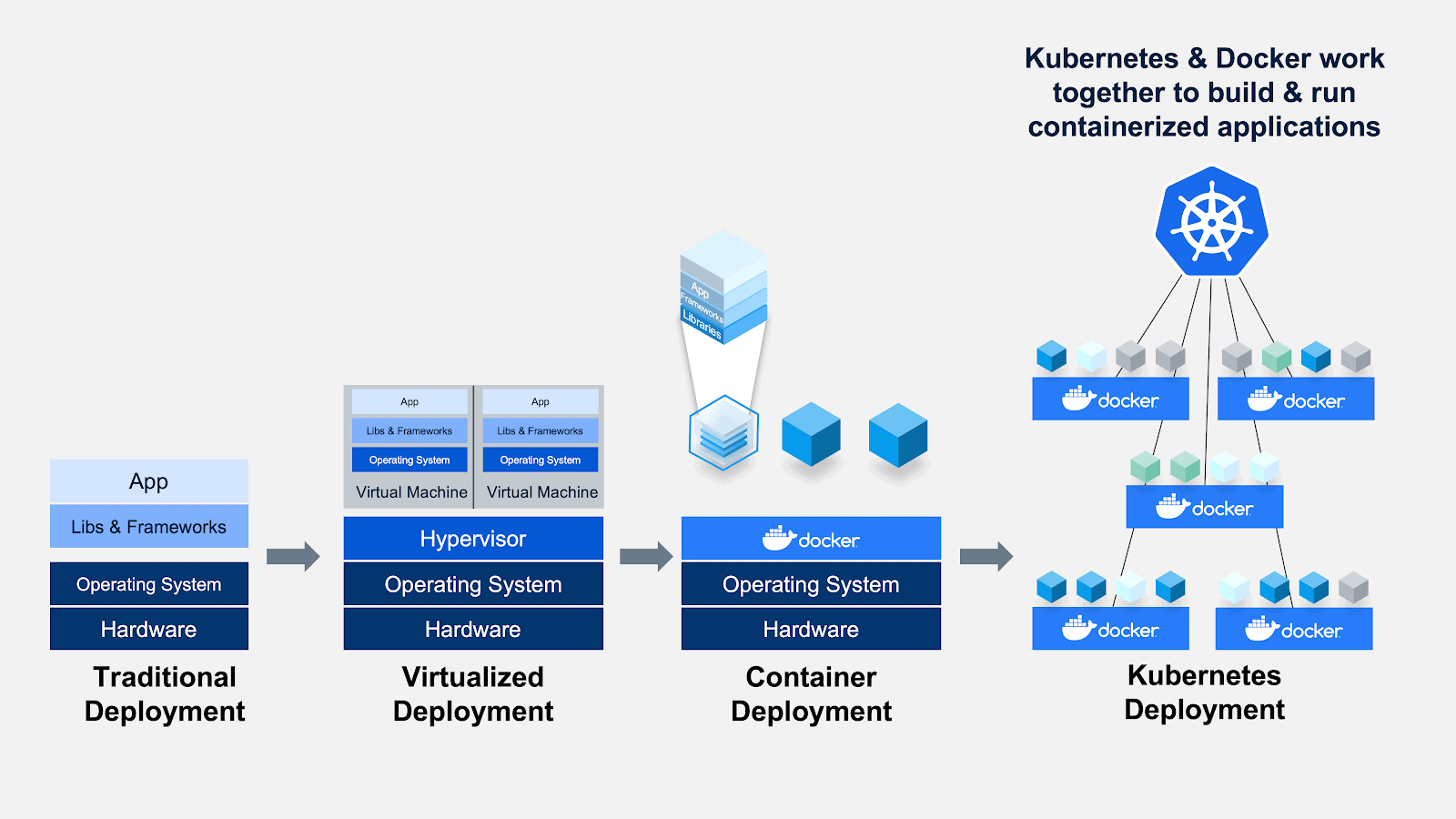
Kubernetest + Docker
Architecture / Components


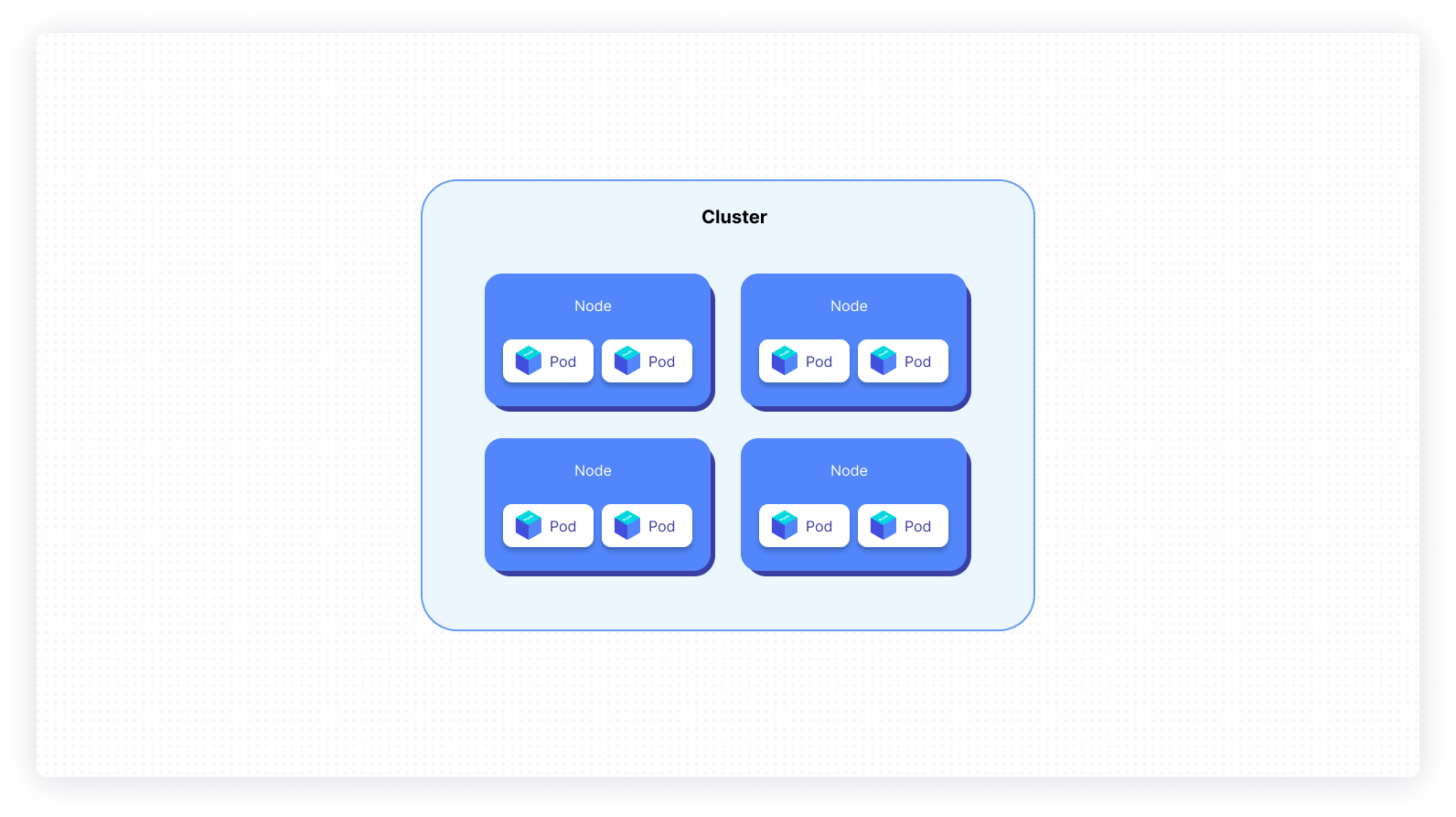
Cluster
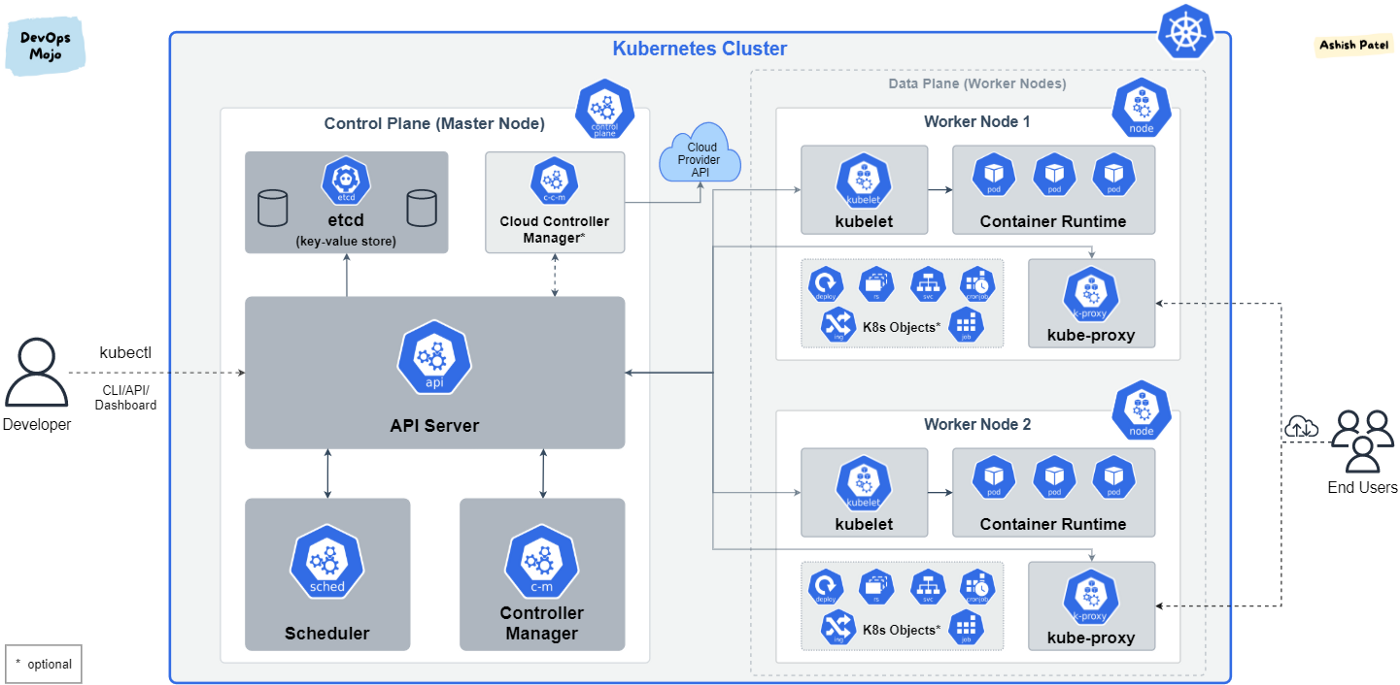
The control plane schedules Pods to run, routes traffic, and handles everything else happening inside a cluster.
Everything inside Kubernetes is running in a cluster, everything managed via kubectl will always be the same, and that things may change externally depending on how your cluster is deployed.
https://www.containiq.com/post/kubernetes-cluster
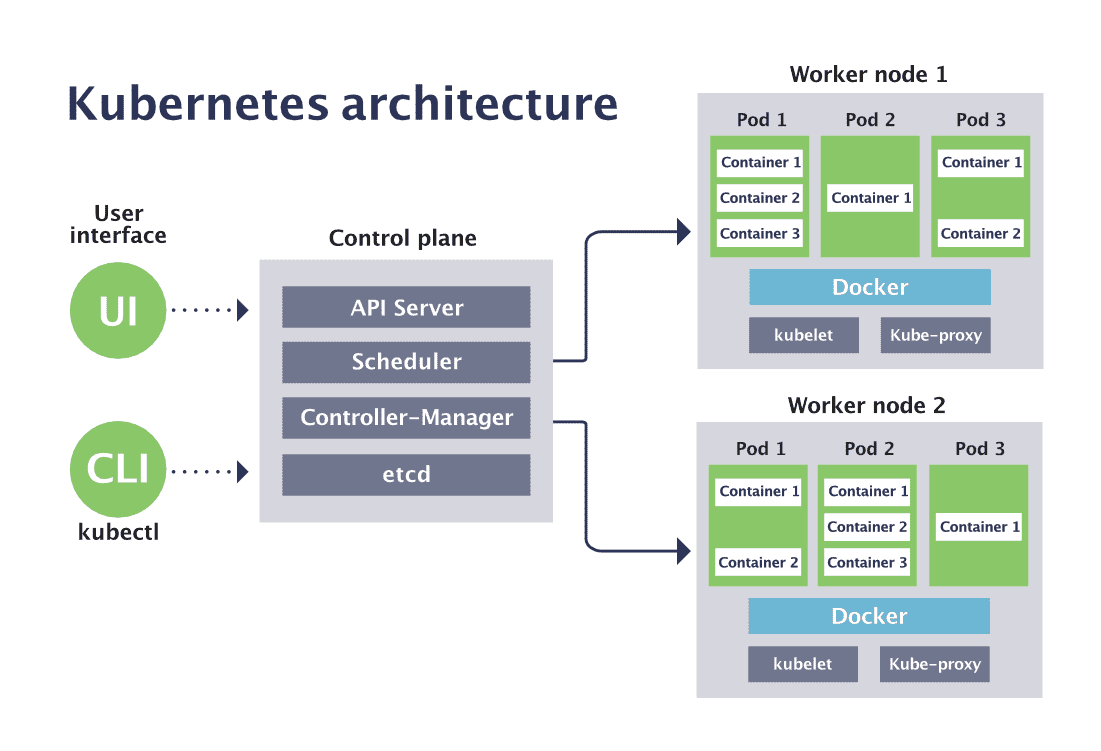
Node
Master Node (Control Plane Node) + Worker Node
Master Node (Control Plane Node)
API Server
The central component in a Kubernetes cluster.
It’s responsible for handling internal and external traffic.
Kube-apiserver is the only component that connects with the etcd database and works as a master component and the frontend of the cluster’s shared state. It’s mainly responsible for handling the API calls that normally handle authentication, authorization, and admission controls.
https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/command-line-tools-reference/kube-apiserver/
Scheduler
- It first checks for the availability of the resources in nodes, and based on the type of request, it assigns one that’s available.
- Worker node will host the pod using different scheduling algorithms.
Scheduling decisions are based on resource availability and other factors like hardware, software, workload, and policy constraints.
- In the case that a node is not suitable for the current pod, the pod will remain unscheduled until there is a node available.
https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/command-line-tools-reference/kube-scheduler/
Controller-Manager
Kube-controller-manager
- It constantly interacts with the kube-apiserver to determine the state of the cluster. If the state is not matched, the manager contacts the necessary controller to match the desired state.
Cloud-controller-manager
It is similar to kube-controller-manager, except that it interacts with the cloud-specific APIs.
As Kubernetes continues to advance, it also handles some of the controller tasks that had been previously handled by the kube-controller-manager.
https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/command-line-tools-reference/kube-controller-manager/
Etcd database
It stores information in the form of key-value pairs such as storing cluster state, networking information, and other persistent information.
Update : When an update is needed, it doesn’t overwrite the pairs; rather, it creates a new entry and appends the end, and marks the previous entry for future removal.
It works with most HTTP libraries and curl.
Worker Node
The worker nodes are where the actual application is deployed.
A node is simply a physical or a virtual machine, depending on the type of cluster you have in your Kubernetes environment.
To containerize your application, you need to put the containers in pods that run on different nodes.
Each node is managed by the kube-apiserver, and scheduling happens via the kube-scheduler, which means each node is under the control of the control plane.
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/architecture/nodes/
Pod
A Pod is similar to a set of containers with shared namespaces and shared filesystem volumes.
Within a Pod’s context, the individual applications may have further sub-isolations applied.
Pods are the smallest deployable units of computing that you can create and manage in Kubernetes.
Every Pod in a cluster gets its own unique cluster-wide IP address. This means you do not need to explicitly create links between Pods and you almost never need to deal with mapping container ports to host ports.
Kubernetes IP addresses exist at the Pod scope - containers within a Pod share their network namespaces - including their IP address and MAC address.
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/pods/
Kubelet
- Kubelet is the part of every worker node that makes sure the containers that need to run are currently running.
- It receives the pod specification as an API call and works to configure the worker node until the specifications are met.
- The most important part is that a kubelet does not manage any container that is not created by Kubernetes.
https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/command-line-tools-reference/kubelet/
Kube-proxy
It manage the network requirements of the node by maintaining an iptable. Communication within or outside the cluster is enabled by Kube-proxy.
Kube-proxy uses an operating system packet filtering layer if one exists and is currently available. Otherwise, kube-proxy itself forwards the traffic.
Features
- Kubernetes expects all communication to the API server to be done over HTTPS.
- You enable service account tokens and at least one other authentication method. Such an authentication method could be Basic Auth or X509 certs.

Network Model
Kubernetes imposes the following fundamental requirements on any networking implementation (barring any intentional network segmentation policies):
- pods can communicate with all other pods on any other node without NAT
- agents on a node (e.g. system daemons, kubelet) can communicate with all pods on that node
Managements
- The most popular managed Kubernetes services.
- Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE), by Google
- Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS), by Amazon
- Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS), by Microsoft
Cheet Sheet
https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/kubectl/cheatsheet/
[Reference] https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/overview/components/

Comments powered by Disqus.